Great Rift Valley: Journey Through Earth's Biggest Scar

Introduction to the Great Rift Valley
Explanation of the Great Rift Valley's geographical significance
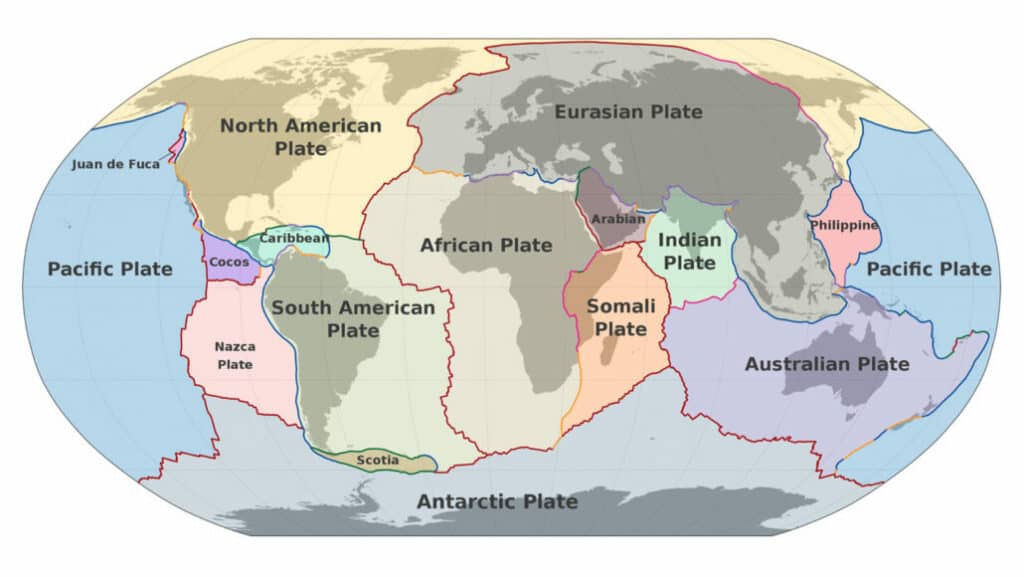
The Great Rift Valley holds immense geographical significance due to its role in the Earth's tectonic activity. It stretches approximately 6,000 kilometres from Lebanon in the north to Mozambique in the south.
The valley consists of interconnected geological formations such as faults, volcanoes, and geothermal activity. The region's diverse landscapes provide habitats for unique flora and fauna that have evolved to adapt to the valley's varied environments.
Overview of the Great Rift Valley's formation
The Great Rift Valley was formed by tectonic plate movements that began around 20 million years ago. The African Plate is slowly splitting into two, creating the East African Rift. This rift has led to the formation of several distinct features, including cliffs, deep lakes, and volcanic mountains. The valley is constantly changing due to seismic activity caused by the interaction of tectonic plates in the region.
The Great Rift Valley continues to be a dynamic geological region, attracting scientists, geologists, and tourists alike who are intrigued by its unfolding geological processes.

Lake Tanganyika in the Great Rift Valley
Characteristics and unique features of Lake Tanganyika
Lake Tanganyika stands out for its remarkable characteristics in the Great Rift Valley. As the world's second oldest and second deepest lake, it spans an impressive length of 673 kilometres and plunges to depths of over 1,470 meters.
The lake's clear blue waters are surrounded by cliffs and lush greenery, creating a picturesque setting that attracts visitors from around the globe. Lake Tanganyika also boasts a unique geological history, with its formation dating back millions of years to the tectonic movements that shaped the Great Rift Valley.
Biodiversity and aquatic life in Lake Tanganyika
Lake Tanganyika is renowned for its rich biodiversity and stunning array of aquatic life. The lake is home to more than 350 fish species, making it a paradise for aquatic enthusiasts and researchers alike. Its diverse ecosystem supports many fish species, including the colourful cichlids that have evolved in isolation within the lake. The waters of Lake Tanganyika also harbour unique crustaceans, molluscs, and other microorganisms that contribute to the lake's ecological vibrancy and scientific interest.
Mount Kilimanjaro in the Great Rift Valley
Description of Mount Kilimanjaro's geological attributes
Mount Kilimanjaro is a majestic sight within the Great Rift Valley, boasting impressive geological attributes. As Africa's highest peak and the world's tallest freestanding mountain, it towers over the surrounding landscape at 5,895 meters.
The mountain is a dormant stratovolcano with three main volcanic cones: Kibo, Mawenzi, and Shira. The glaciers atop Mount Kilimanjaro are distinctive features that have been retreating in recent years, highlighting the effects of climate change on this iconic landmark.
Climbing and trekking opportunities on Mount Kilimanjaro
For adventure enthusiasts, Mount Kilimanjaro offers exhilarating climbing and trekking opportunities. Various routes cater to different skill levels and preferences, allowing climbers to choose between the Marangu, Machame, Lemosho, and other trails.
While scaling the peak is a challenging endeavour due to altitude and changing climate zones, it rewards climbers with breathtaking vistas of the Great Rift Valley below. Experienced guides and porters assist trekkers in navigating the mountain safely and provide insights into the local flora, fauna, and cultural significance of Mount Kilimanjaro.

Ngorongoro Crater in the Great Rift Valley
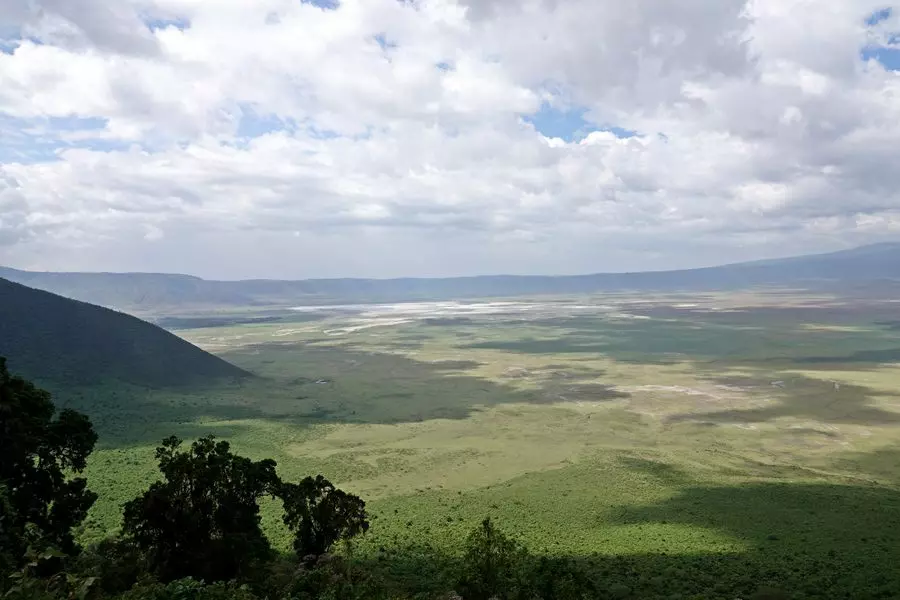
Geological formation and history of Ngorongoro Crater
Ngorongoro Crater is a remarkable geological formation in the Great Rift Valley, renowned for its rich history and unique attributes. Created by the collapse of a massive volcano millions of years ago, the crater spans approximately 260 square kilometres and reaches depths of up to 600 meters. Its diverse ecosystems support a wide array of flora and fauna, making it a UNESCO World Heritage Site and a vital component of the Ngorongoro Conservation Area.
Wildlife conservation efforts and animal species in Ngorongoro Crater
Visitors to Ngorongoro Crater witness extensive wildlife conservation efforts that have helped preserve the area's biodiversity. The crater is home to many animal species, including the iconic Big Five: lion, leopard, elephant, buffalo, and rhinoceros.
Other species, such as zebras, wildebeest, and hippopotamuses, roam the grassy plains alongside numerous bird species. Conservation initiatives strive to protect these animals and their habitats, ensuring the continued existence of this natural wonder.
Serengeti National Park in the Great Rift Valley
Overview of the Serengeti National Park's ecosystem
Serengeti National Park is a prime example of a well-preserved ecosystem within the Great Rift Valley. Covering approximately 14,750 square kilometres, the park boasts a diverse range of habitats, from grassy plains to riverine forests.
The park is famous for its annual wildebeest migration, where millions of these animals traverse the plains in search of greener pastures. This spectacle attracts visitors from around the globe, eager to witness nature's impressive display in this natural haven.
Safari experiences and wildlife encounters in the Serengeti
Exploring Serengeti National Park offers unparalleled safari experiences and unforgettable wildlife encounters. Visitors have the opportunity to spot a plethora of wildlife species, including the Big Five - lion, leopard, elephant, buffalo, and rhinoceros.
Additionally, the park is teeming with other fascinating animals, such as giraffes, cheetahs, and hyenas. The diverse birdlife further enriches the safari experience, with numerous species gracing the skies above. Guided tours and game drives provide insights into the park's ecosystems and offer close-up encounters with its inhabitants.

Maasai Mara National Reserve in the Great Rift Valley
Cultural significance of the Maasai Mara tribe
Visiting the Maasai Mara National Reserve offers a glimpse into the rich cultural heritage of the Maasai tribe. The Maasai people, known for their vibrant traditional attire and unique customs, continue to uphold their age-old traditions amidst modern influences.
Interactions with the Maasai community provide visitors with insights into their nomadic way of life, deep connection to the land, and enduring values that have sustained their society for generations.
Annual wildebeest migration and conservation initiatives in Maasai Mara
Experience the awe-inspiring phenomenon of the Annual Wildebeest Migration in the Maasai Mara National Reserve. Witness thousands of wildebeest and zebras crossing the Mara River, braving crocodile-infested waters in search of fresh grazing lands. Conservation efforts in the reserve focus on preserving this natural spectacle and maintaining the delicate balance of its ecosystems.
By supporting sustainable tourism practices and community-led initiatives, visitors can contribute to the conservation of this biodiverse region.

Lake Turkana in the Great Rift Valley
Features and characteristics of Lake Turkana
Exploring Lake Turkana unveils a landscape of striking beauty and unique features. Known as the world's largest desert lake, Lake Turkana mesmerizes visitors with its azure waters contrasted with the surrounding arid terrain.
The lake's alkaline nature supports diverse wildlife, including Nile crocodiles and countless bird species. Its volcanic origins add an interesting geological dimension to the area, making it a fascinating destination for nature enthusiasts and adventurers alike.
Paleontological discoveries and archaeological sites around Lake Turkana
Your journey around Lake Turkana will lead you to remarkable paleontological sites that have yielded invaluable insights into human evolution. The region's rich fossil deposits have revealed ancient hominid remains, contributing significantly to our understanding of early human history.
Additionally, numerous archaeological sites near the lake bear witness to past civilizations and cultures that thrived in this region. By immersing yourself in these discoveries, you can delve into the deep-rooted history of Lake Turkana and appreciate its significance in shaping our collective heritage.
Hell's Gate National Park in the Great Rift Valley
Activities and attractions in Hell's Gate National Park
Visiting Hell's Gate National Park opens up a world of exhilarating activities and awe-inspiring attractions. The park's diverse landscape offers hiking, rock climbing, and even cycling opportunities among remarkable rock formations and geothermal vents.
Birdwatchers can delight in spotting various bird species, while wildlife enthusiasts may catch a glimpse of zebras, gazelles, and elands roaming freely. Exploring the gorges and hot springs within the park provides a unique way to connect with nature and experience the untamed beauty of this iconic location.
Geothermal phenomena and unique landscapes in Hell's Gate
Hell's Gate National Park stands out for its geothermal wonders and distinctive landscapes that set it apart from other conservation areas. The park's geothermal activity manifests through hot springs, steam jets, and geysers, creating a surreal atmosphere that captivates visitors. The towering cliffs, gorge walks, and volcanic plugs add a sense of grandeur to the surroundings, offering a surreal backdrop for exploration and adventure.
By immersing yourself in the geothermal phenomena and unique landscapes of Hell's Gate, you can witness the raw power of nature and appreciate the park's extraordinary natural heritage.
